
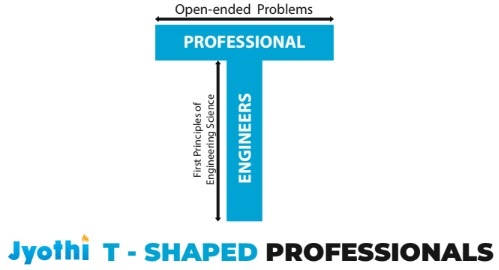
Jyothi Engineering College prepares students to become T-Shaped professionals, i.e., professionals who have in-depth expertise in their discipline as well as a breadth of competencies required in the twenty-first century. Industry seeks engineers with these skills. The vertical bar on the T-shaped professional is an indication of the depth of knowledge and skills in their chosen engineering stream whereas the horizontal bar represents the person's competencies in interdisciplinary areas and life skills. This contextual knowledge helps in giving students a broader perspective. T-shaped skills – or a T-shaped professional – has qualities that make that personnel more versatile and valuable as they possess excellent knowledge and skills in specific areas and are good at working with others in a collaborative way.
In order to train our students to become “T” shaped professionals, so that they are “future ready”, we have set up an incubation Centre, Integrated Industrial Incubation Centre (IIIC), in association with TATA Technologies.
Strategy & Consulting
Business Process
Marketing Rules
Partnerships




5m+ Trusted
Global Customers
Project Complete
Years Of Experience
Team Members

ASSOCIATE DIRECTOR

MANAGER

MANAGER (IEC)

SENIOR TRAINER

TRAINER

INSTRUCTOR
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Harum atque soluta unde itaque. Consequatur quam odit blanditiis harum veritatis porro.
View All ActivitiesIIIC has conducted training in Electric Vehicle Technology for the Institute of Printing Technology & Government Polytechnic College, Shoranur. Rev Fr.... Read More
2022
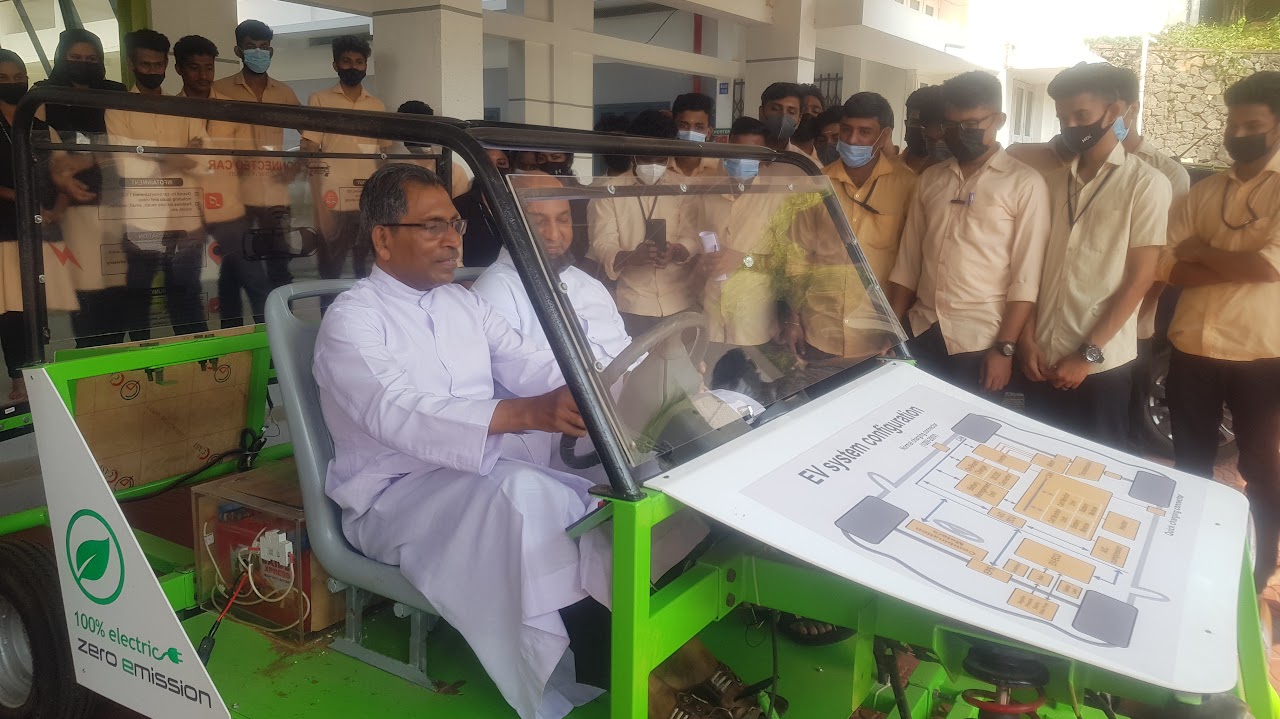

IIIC has taken an initiative to conduct collaborative training programs in association with various professional bodies like IEEE, ISTE, IE(I). One such program on Electric Vehicle Technology was conducted on 13-04-2022 for JECC students. Read More
2023

2023
.jpg)